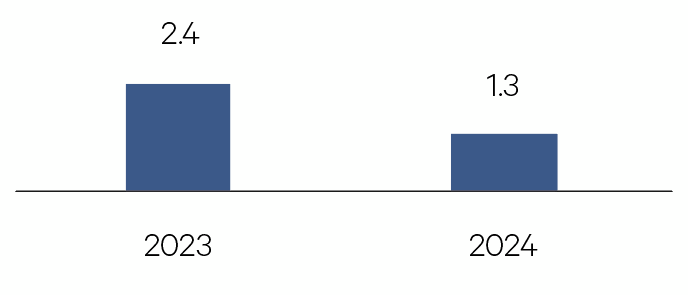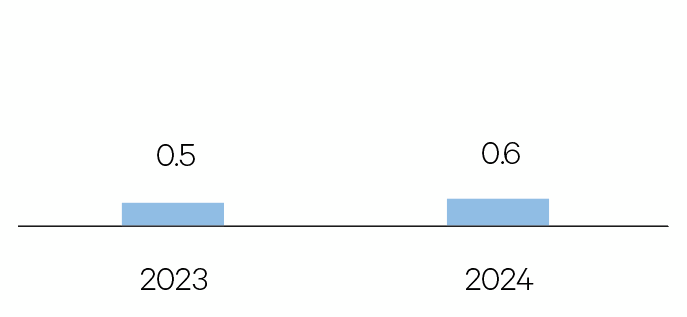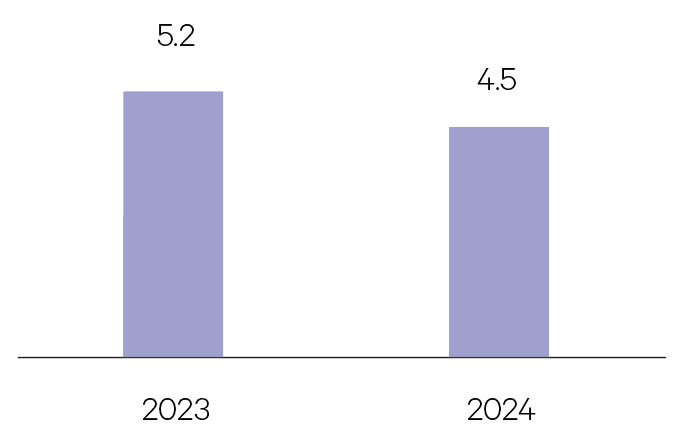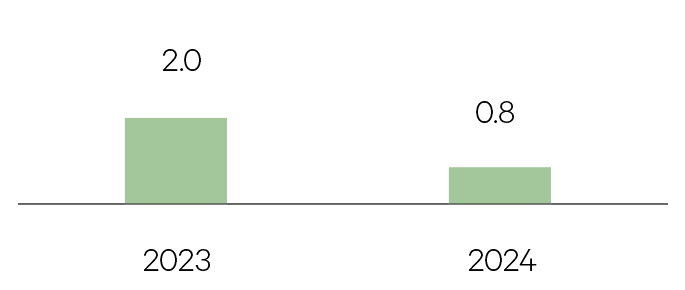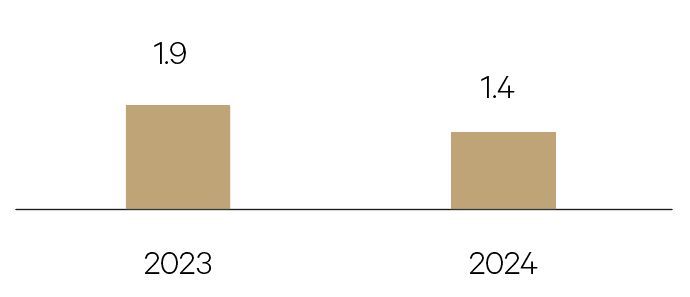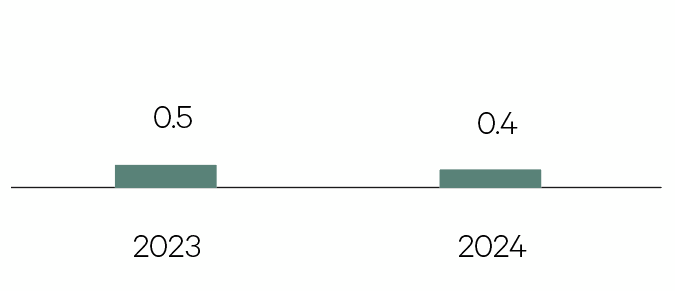-
United States

US economic growth will ease following a surprisingly strong 2023. Surplus COVID-19 savings have depleted, monetary policy is less easy and fiscal policy is less supportive. A weaker labour market will see consumption pullback and inflation continue to ease.
GDP %

-
Europe

Real GDP growth in the euro area is expected to remain weak in 2024. Countries with a high proportion of industrial production, such as Germany, must expect lower growth on the back of a still soft outlook for China and rising trade protectionism.
GDP %

-
China

We remain cautious on China in the coming year, with a high downside risk driven by the property sector. The correction in the real estate sector is likely to continue in 2024 and weigh on investment, household consumption and local government finances. Fiscal support is limited by already excessive levels of debt.
GDP %

-
Japan

The Japanese economy is expected to decelerate in 2024 on the back of slowing domestic and external demand. Softer growth in the US and China will weigh on exports, which will also slow manufacturing. On the back of growing economic uncertainties, companies are expected to limit their investment.
GDP %

-
Australia

Higher interest rates will slow the economy in 2024. Employment growth is expected to remain positive, but the unemployment rate will move up. A slowdown in net migration will help restore some balance to the housing market. Consumer spending and inflation will decelerate.
GDP %

-
United Kingdom

Real (inflation adjusted) disposable income is set to improve as inflation falls but wage growth remains elevated. Fiscal policy is likely to weigh on growth as the government’s COVID-19 and energy support measures continue to unwind.
GDP %